What is a website?
Understanding Website: What Are They and How Do They Work?
In today’s digital age, websites have become a staple for businesses, individuals, and organizations alike. But what exactly is a website, and how does it function? Let’s go deeper into this modern phenomenon.
Website:
Website is a collection of interconnected web pages, grouped under a common domain name and accessible via the internet. It serves as a digital platform where users can access information, interact with content, or perform specific online tasks, such as shopping or social networking.
1. Content: This constitutes the heart of any website. It’s the combination of text, images, videos, and other media forms that provide value and information to the website’s visitors.
For example: Kaffe Codes Bakery
-
- Text: Descriptions of the bakery, its history, menu items, and customer testimonials.
- Images: Photos of baked goods, the bakery’s interior, staff, and happy customers.
- Videos: A short documentary on how Kaffe Codes Bakery started, tutorials on baking, and customer reviews.
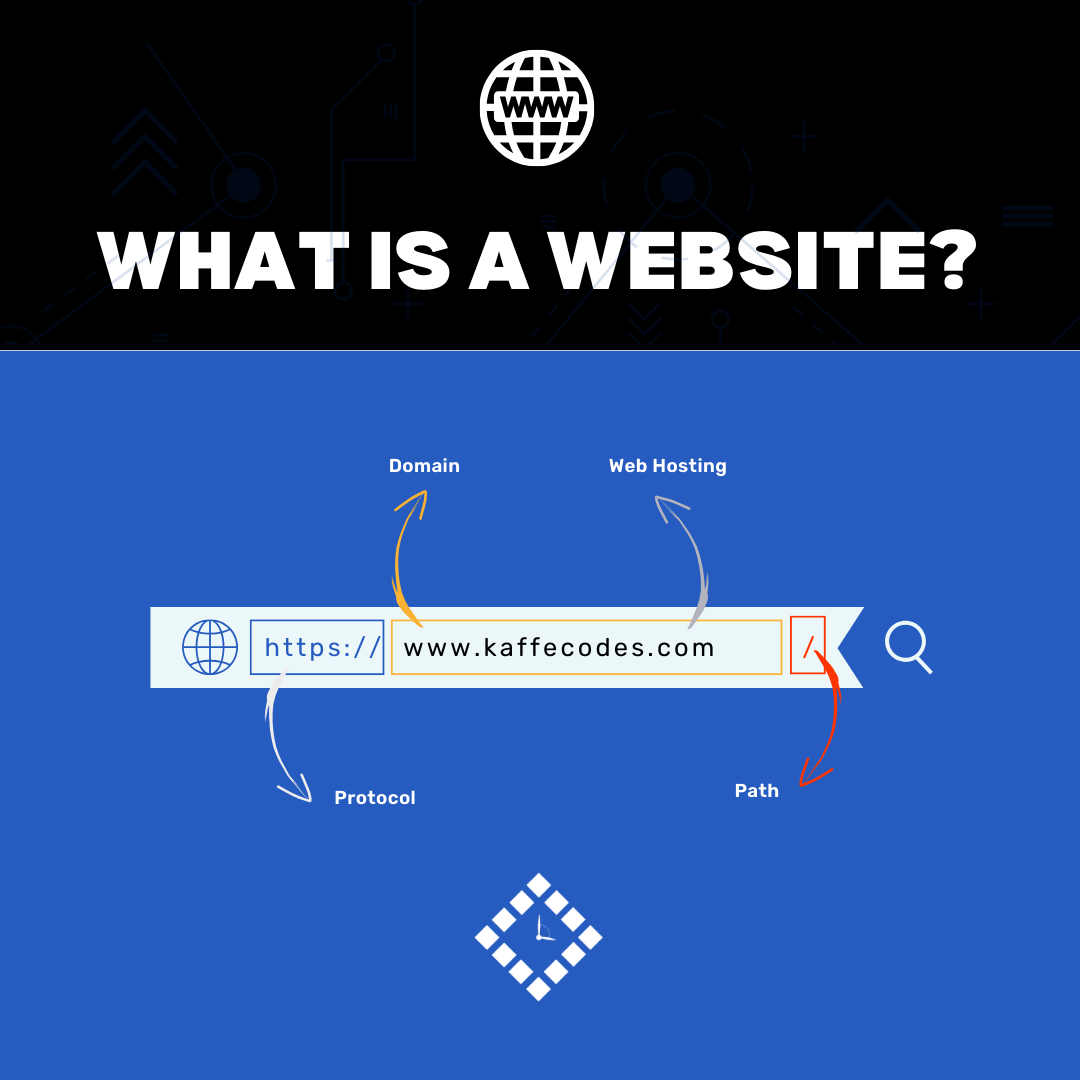
2. URL (Uniform Resource Locator): Think of this as the address of the website. Every website has a unique URL that users input into their web browsers to access the site.
For examples: https://www.kaffecodes.com
3. Web Hosting: Just like a shop needs physical space to display its products, a website requires digital space to store its files. This digital space, offered by servers, is known as web hosting.
For example: kaffecodes.com, Kaffe Codes Bakery might use a popular hosting service like Bluehost or SiteGround to store their website files and make them accessible to users around the world.
4. Domain Name: The unique identifier for every website.
For example: In the web address https://www.kaffecodes.com/, “kaffecodes.com” is the domain name.
5. Web Pages: The individual sections or “pages” of a site that users navigate through, each serving a specific purpose or topic.
For example:
-
- Homepage: Introduces the bakery, showcasing bestsellers and latest news.
- Menu Page: Lists all the bakery items available, categorized by type (cakes, bread, pastries).
- About Page: Tells the story of Kaffe Codes, the founder, and the bakery’s history.
- Contact Page: Provides the bakery’s address, contact number, an inquiry form, and a map.
- Shop Page: Allows users to order bakery items online and have them delivered.
- Blog Page: Regular posts about baking tips, ingredient sources, and more.
6. Navigation: This helps users traverse through different parts of a website, typically via menus or links.
For example: A top menu bar with links to: Home, Menu, About, Shop, Blog, and Contact.
A footer menu with links to: FAQ, Terms of Service, Privacy Policy, and Social Media icons.
7. Design & Layout: The aesthetic and structural aspect of a website, crafted using tools and languages like CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) and HTML (HyperText Markup Language).
For example:
- A soft, pastel color scheme reminiscent of cakes and icing.
- A clean, easy-to-read font.
- Mobile-responsive design ensures the website looks good on both desktops and mobile devices.
- Engaging visuals of bakery items to entice users.
Static vs. Dynamic Websites
Static Websites: Simple and unchanging, the content of these sites remains consistent unless manually altered by the developer or webmaster. They are often built using just HTML and CSS.
Dynamic Websites: As the name suggests, these are adaptable platforms. Their content can alter in real-time, driven by factors like user interactions, location, or time. They usually involve more intricate technologies, including server-side programming and databases.
Conclusion
Websites are integral to our online experience. From providing information to offering services, they cater to a myriad of needs. As the internet continues to evolve, understanding the basics of websites, from their structure to their functioning, remains crucial for anyone navigating the digital world.